The curious behavior in Saudi law is one of the legal concepts that contribute to the organization of transactions and legal relations between individuals This behavior is manifested in certain cases when a person takes legal action for the benefit of another person without having authorization or permission from this person The curious behavior is one of the actions of self-management where the person interferes in the affairs of others with a desire to improve their situation or to save them from a difficult situation Although the intention in these actions is positive, there are Legal effects that may result from this type of behavior, which can directly affect the rights of non-contracting parties, so in this article, we will review the concept of curious behavior and how it affects the rights of different parties by Saudi law.
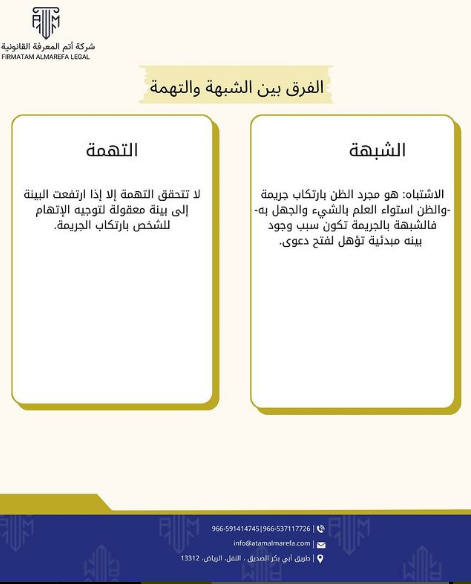
| Charge A charge is only established if the evidence rises to a reasonable belief that the person is guilty of the offense. |
| Suspicion Suspicion is the mere suspicion that a crime has been committed.- Suspicion is the equality of knowing something and not knowing it. Suspicion of a crime is the reason there is preliminary evidence to open a case. |
Definition of Curious Behavior in Saudi Law
Curious behavior refers to actions taken by a person to manage the affairs of another person without having the legal authority to do so. In this context, curious behavior can be embodied in cases such as paying another person’s debts or making decisions on his behalf without his consent. Curious behavior is considered a legally unjustified act and therefore has no legal consequences, such as contractual acts, unless it is subsequently recognized by the person in whose interest such acts are made. It is not legally justified and therefore does not have legal effects like contractual acts unless it is subsequently recognized by the person for whose benefit it is done in certain cases. Curious acts may be positive if they benefit the affected person, However, it can also cause harm if it is not favorable or does not take into account their rights or interests.
The legal effects of curious behavior on non-contracting parties
The legal implications of curious behavior on the rights of non-contracting parties are numerous, as these behaviors can lead to a range of consequences that may be positive or negative, the most prominent of which are
Non-recognition of curiosity acts as a legal contract, as curiosity acts do not result in binding obligations for the parties involved unless the person who performed the act has authorization or permission from the other person, the curiosity act itself is not legally recognized.
Possibility of claiming compensation for damages If the curious behavior causes damage to the person concerned, he can claim compensation for any losses or damages resulting from this behavior, which provides protection for his rights and reflects the importance of legal supervision of these behaviors.
Conditions for the validity of curious behavior in Saudi law
For curious behavior to be valid and its effects to be legal, several conditions must be met, most notably:
The act must be done for the benefit of the other person without having legal authorization or permission from that person.
The intention of the person acting must be positive and aimed at achieving the interest of the person for whose benefit the act was done.
The act must be logical and appropriate to the other person’s circumstances and must not cause damage to the other person.
These conditions emphasize the importance of the need for precision in managing curious behavior to achieve the desired goals without causing negative effects that may affect the rights of the parties involved.
The difference between a fiduciary act and a contractual act
Curious conduct is a different type of legal conduct compared to contractual conduct. Curious conduct differs from contractual conduct in several ways.
A contractual act requires an agreement between two parties, while a fiduciary act is done without any prior agreement.
The legal effects of a contractual act are binding on all parties, while a curious act does not produce binding legal effects unless it is recognized by the party for whose benefit the act is performed.
Contractual conduct is based on the common will of the parties, while curious conduct shows the individual will of one person to manage the affairs of another.
This difference reflects the importance of understanding the nature of a fiduciary act and how it affects the parties involved, especially in a diverse legal environment.
Conclusion
Although it may involve some risks and negative effects on non-contracting parties, it has an important role in facilitating positive actions and behaviors in the interest of others, and by recognizing the rights of parties affected by curious behavior, the protection of rights and the achievement of justice in legal transactions can be strengthened. While recognizing the importance of this type of behavior, individuals must be cautious in implementing curious behavior and avoid causing harm to others, which reflects the importance of legal awareness and the need to adhere to legal principles. Regulating these behaviors ensures the safety of relations between individuals and contributes to protecting rights and promoting social and economic stability in the Kingdom.
